Tactile Memory with Soft Robot: Tactile Retrieval-based Contact-rich Manipulation with a Soft Wrist
CoRL 2025 Workshop on Dexterous Manipulation: Learning and Control with Diverse Modalities
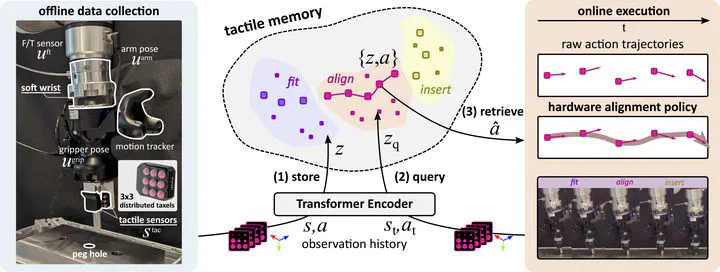
Tactile memory—the ability to store and retrieve touch-based experiences—is critical for humans to perform contact-rich and fine manipulation tasks like key insertion, even under uncertainties. Replicating this capability in robots remains challenging due to underdeveloped spatiotemporal representations for tactile signals. This study introduces TaMeSo-bot (Tactile Memory with Soft Robot), a robotic system that combines physical softness for safe contact with retrieval-based manipulation. Inspired by neurophysiological findings on tactile memory, TaMeSo-bot introduces a transformer-based method that processes multi-modal sequences—including tactile, force-torque, and proprioceptive signals—while modeling the spatial relationships across distributed taxel sensors. Leveraging a masked token prediction technique, our system autonomously extracts task-relevant features without manual subtask segmentation. We validate our approach on peg-in-hole tasks in both offline and real-robot experiments. Results show improved action position retrieval accuracy (34% over baseline) and performance with 77.5% and 57.5% success rates under seen and unseen conditions (peg and hole pose uncertainty and different diameter pegs), respectively.